Scar Revision
Hair transplant procedures that use follicular units exclusively leave no visible scarring in the recipient area. In Follicular Unit Transplantation(FUT), there is a single thin line in the donor area where the strip was removed. In Follicular Unit Extraction(FUE), there are multiple tiny round, white scars in the donor area, one for each extracted follicular unit. Generally, these scars are undetectable and are of no cosmetic consequence to the patient.
When older methods of hair restoration surgery are used, current techniques are performed improperly or, less commonly, when a patient is a poor healer, scarring may be excessive and may present a cosmetic problem. The scarring may be due to the plug itself (which invariably leaves a round white scar), it may be caused by the elevation or depression of grafts (seen with some slit and minigrafting techniques), or it may be due to a stretched or thickened donor scar.
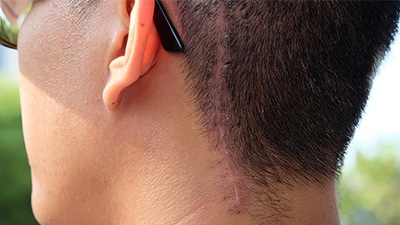

Scarring in the recipient area can be eliminated by keeping recipient sites very small. Sites less than 1.2 mm, such as those used in FUT and FUE, will not leave any visible marks. Scarring in the donor area can be minimized by meticulous closures, where the wound edges are perfectly approximated and are under little or no tension. Using an inert material to close the wound, such as stainless steel staples, also helps to minimize the destruction of hair follicles and the incidence of hair transplant scarring.
When significant scarring does result, a number of techniques are available to reduce it. The two most effective methods are scar revision (excising or changing the direction of a hair transplant scar) and camouflage (a technique where hair is transplanted directly into the scar). In addition, thickened scars may be flattened with cortisone injections, depressed scars may be raised with dermal fillers and an irregular surface may be made smoother with dermabrasion or laser treatments.
The method for fixing hair transplant scars must be tailored to the specific situation, since each hair transplant repair patient has unique problems which influence the approach. Perhaps the most significant issue is the amount of remaining donor hair reserves. The following examples illustrate a number of common techniques used to improve scarring.
The open-donor removal of plugs from the donor area leaves round, white scars. If a person has sufficient scalp laxity (looseness), the area where the plugs have been removed can be improved by simply excising these scars in the same manner that a donor strip is removed. After the area is sutured closed, the hair in the excised tissue can be dissected out under microscopic control and serve as a source of additional grafts.
Concerned About Your Hair Loss Troubles?
Set aside those worries, for now, we at NU/HART Philippines are more than happy to help you deal with this problem. All you have to do is send your inquiries to: info@nuhartclinic.com.ph
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Stay in touch with us to get latest news and special offers.
Why NU/HART?
These numbers speak for themselves!